Plastic Surgery or any type of surgery will always come with a risk of bruising and swelling.
The amount of bruising depends on.
- Types of surgery performed
- Individual ability to heal
- Degree of Invasiveness
- Experience of Surgeon
Plastic Surgery After Care
When recovering from plastic surgery all that is mentioned above will make a difference in the time to recover and outcome of surgery.
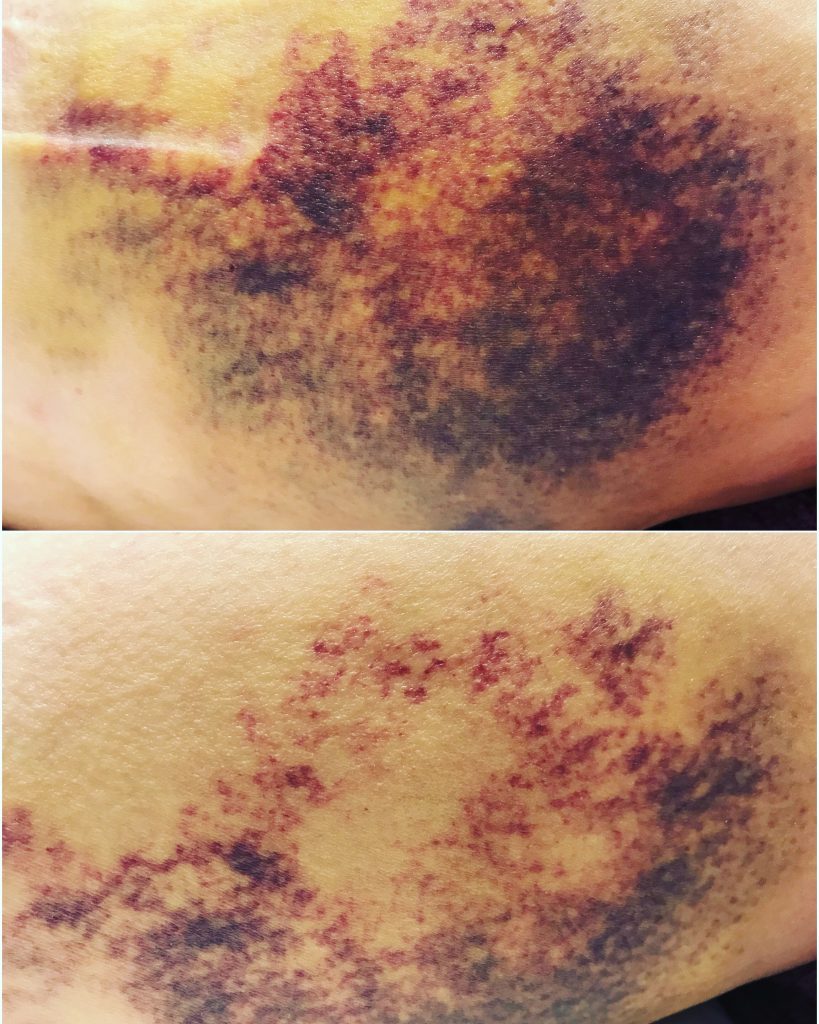
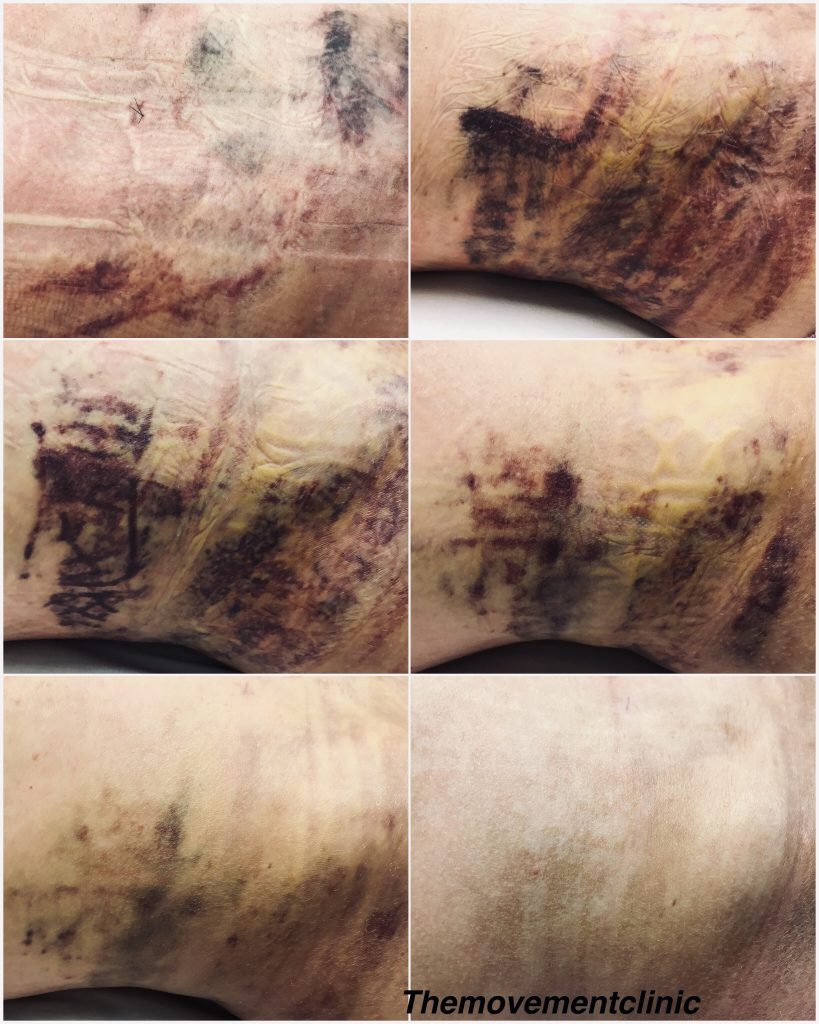
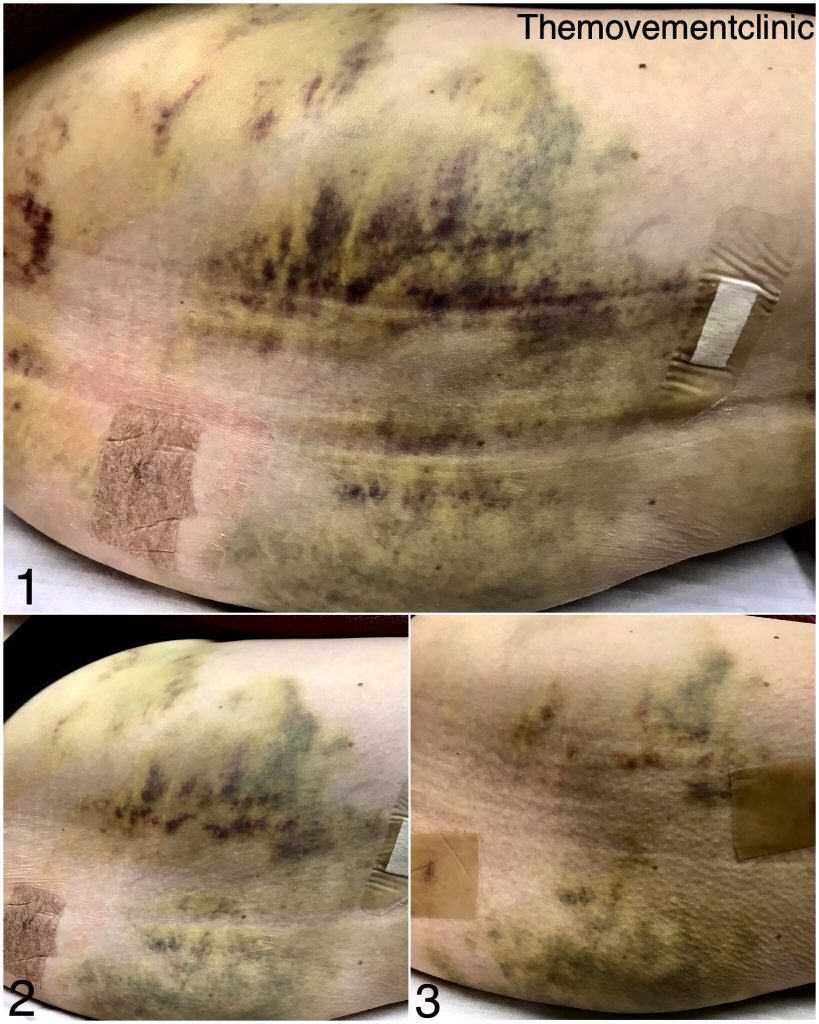
Many types of plastic surgery especially Liposuction which is one of the most common will cause bruising. Different methods like smart liposuction is less invasive will cause minimal bruising and swelling, compared to the traditional sculpting way, which is invasive and causes excessive bruising and swelling.
An effective qualified manual lymphatic drainage therapist will help to reduce the risk of seroma’s, scar formation and effective closure of wounds and general health.
Bruising and Swelling Post Surgery
What is a bruise?
A bruise is the cause of blood capillaries leaking into the underlying tissue of the skin, this could be due to blunt force trauma or blood coagulation medical issues. A bruise can also be called a contusion or haematoma and is categorised into three sections, subcutaneous, intramuscular or periosteal.
Subcutaneous bruise: Located just underneath the layer of skin of minor origin and usually not associated with a great deal of pain and only lasts for a couple of days.
Intramuscular bruise: Located in the belly of the muscle, usually created with a more powerful impact, swelling and nerve pain can also be present, damage to muscle and pooling of blood can travel underneath the skin creating a much larger radius of the bruise.
Periosteal bruise: The deepest of a bruise effects the outer layer of the bone can be associated with a fracture.
Intramuscular and Periosteal could also be associated with a severe contusion (bruise) and can lead to health complications. Some severe bruises may lead to pain associated with swelling and nerve damage due to compartment syndrome. (compartment syndrome could be due to encapsulated haematoma blood pooling) blood clots within the muscle belly, organ contusions caused by trauma, or haemorrhaging.
Medical conditions could also exacerbate a bruise and bleeding, medication, age and vitamin deficiencies can also be a factor in how a bruise can heal.
What happens when we bruise?
Traumatic external forces can cause blood vessels to tear and leak into the spaces between the skin and muscle creating a bruise. Depending on the trauma this may also damage lymph vessels, pain and swelling makes the lymph system contract.
When the lymphatic system exceeds its working load, meaning the amount of swelling and molecular debris in the tissue spaces continues to spread. As the lymph vessels are reduced in its working capacity, blood flowing to the site of injury can slow, nerve sensations are reduced causing numbness and scar tissue develops.
Due to pain and swelling, muscle and joint movements become difficult placing more stress and compensation on other functioning muscles and joints.
With manual lymphatic drainage the aim is to reduce bruising and swelling:
- Alleviates pain,
- Restore skin tone,
- Increase muscle and nerve function,
- Reduce rehabilitation time.
Severe bruising could cause life threatening complications in some patients. A medical assessment of these bruises should be sought before any treatment of manual lymphatic drainage is performed, once this is done lymphatic drainage can be performed once the bleeding stops.
The Movement Clinic has treated bruising from minor to severe trauma, situations where some bruising may occur that has been treated by the movement clinic are:
Post Surgery, Combat Sports, Medical Conditions
The below photo’s are taken before and after manual lymphatic drainage to reduce bruising and swelling for liposuction surgery: Recommended number of MLD treatment sessions is from 4 to 8 lasting from 45min to 1 Hour, depending on the kind of surgery that was performed.